When it comes to offshore outsourcing, achieving cultural harmony entails a shared set of values and beliefs in the workplace among you, your outsourcing partner, and the individuals they recruit for your offshore development team. This harmonization extends to various pivotal elements, encompassing language, business practices, work ethics, and even social norms.
The alignment of cultures plays a crucial role in the expansion and success of your business project management. By fostering such alignment, you can effectively address the typical challenges associated with managing a remote overseas team and a define development methodology. When you and your remote outsourced teams share a common cultural framework with indirect and direct communication it not only eases your concerns but also provides a solid foundation for your company’s growth.
This alignment offers the assurance that your offshore team and members can collaborate seamlessly and exchange ideas, thus establishing regular communication and minimizing misunderstandings and real-time communication breakdowns. It essentially lays the groundwork for a more efficient and productive working relationship between onshore and offshore teams, ultimately enhancing the overall success of your outsourcing initiatives.
Cultural Insights: A Cornerstone of Outsourcing Success
Culture, a blend of shared values, beliefs, and behaviors, profoundly shapes how groups live and work. In the realm of global outsourcing, businesses often grapple with cultural disparities that influence work processes and communication. These disparities between high context cultures can manifest through language barriers, distinct work methodologies, and differing business customs.
Mastering Cultural Competence: A Vital Requirement
Understanding the Outsourcing Partner’s Culture
Success in outsourcing demands a profound understanding of cultural nuances, necessitating a thorough examination of your outsourcing partner’s cultural landscape. This knowledge encompasses studying their norms, practices, local customs, and language.
Bridging the Communication Chasm
Developing Cross-Cultural Communication Skills
Effective cross-cultural communication skills become paramount when outsourcing globally. These skills encompass a comprehensive grasp of communication intricacies within diverse cultures, including language tone, style, vocabulary, and the cultural context in which communication occurs. Developing these skills is pivotal in surmounting language barriers and cultural competency and fostering effective communication.
The Power of Embracing Diversity
Fostering Innovation Through Cultural Diversity
An integral facet of managing cultural differences in outsourcing is the wholehearted embrace of diversity. This signifies not only recognizing but also valuing the distinctions in culture, language, and work styles. Embracing diversity fuels innovation, creativity, and the forging of robust relationships between businesses and outsourcing partners.
Building Blocks: Trust and Respect
Cultivating Trust and Respect
Trust and mutual respect are the cornerstones of successful outsourcing partnerships, particularly in cross-cultural scenarios. Demonstrating cultural sensitivity and understanding is paramount to building these essential foundations. This can be achieved through respect for the provider’s culture, transparent and clear communication throughout, and a willingness to adapt to cultural disparities.
Harmonizing Conflict Resolution
Managing Conflict with Cultural Sensitivity
Cultural disparities can give rise to conflicts within outsourcing relationships. Effective conflict management to improve efficiency requires a well-defined process rooted in open and direct well versed communication, regular meetings or daily roundup meetings, active listening, and a genuine willingness to understand and respect cultural differences. Avoiding stereotypes and focusing on the underlying causes of conflict are crucial for finding mutually beneficial solutions.
The Global Outsourcing Landscape
In this section, we will delve into the dynamic world of global outsourcing, examining the industry’s overarching framework, identifying key players, and exploring the pivotal role that culture plays in the outsourcing ecosystem.
Overview of the Global Outsourcing Industry
The global outsourcing industry has evolved into a multifaceted and expansive landscape that plays a fundamental role in the modern business environment. This subsection will provide an in-depth look at the industry, encompassing its definition, growth, and the diverse range of services that it encompasses. Key points to be covered include:
- Definition of Global Outsourcing: A concise definition of global outsourcing and its significance in today’s business world.
- Historical Perspective: A brief historical overview, tracing the industry’s evolution from its inception to its current state.
- Scope and Diverse Services: An exploration of the vast array of services outsourced, from IT and customer support to finance and human resources.
- Global Market Size: An overview of the market’s size, growth trends, and its economic impact worldwide.
- Geographical Distribution: A look at the distribution of outsourcing hubs and emerging destinations across the globe.
Key Players and Emerging Trends
Major Players: Driving the Outsourcing Landscape
In the ever-evolving global outsourcing landscape, we spotlight the industry’s heavyweights and innovative disruptors. These prominent players shape the industry with their distinct areas of expertise, global reach, and transformative contributions. This section will delve into:
- Leading Companies: An exploration of the global outsourcing giants, including companies like IBM, Accenture, and TCS, along with a focus on their diverse service offerings.
- Niche Specialists: A look at specialized outsourcing firms that excel in specific domains, contributing their expertise to niche sectors.
- Startups and Innovators: Highlighting the entrepreneurial ventures that bring fresh perspectives and agile solutions to the outsourcing industry.
Emerging Trends: The Shifting Landscape
The global outsourcing industry is in a state of constant flux, influenced by an array of dynamic trends and shifts. In this section, we examine these trends and their transformative impact on the outsourcing ecosystem. Key components include:
- Automation and AI Integration: The ever-expanding role of automation, artificial intelligence, and machine learning in streamlining outsourcing processes, reducing costs, and enhancing efficiency.
- Digital Transformation: An exploration of the journey towards digitalization, where businesses are reshaping their operations through technology adoption.
- Global Economic Impact: An analysis of how global economic conditions, trade policies, and geopolitical factors influence the outsourcing landscape.
- Sustainability and CSR: The increasing emphasis on sustainability and corporate social responsibility in outsourcing, as companies align their practices with global environmental and social goals.
Market Competition: The Competitive Dynamics
Competition in the outsourcing industry is fierce, with established players vying for market share and emerging companies seeking to disrupt the status quo. This part of the section delves into the company and competitive dynamics, including:
- Market Share Analysis: An examination of the market shares of key players, shedding light on their relative strengths and market penetration.
- Strategies for Market Domination: An exploration of the tactics and strategies employed by leading outsourcing firms to maintain their competitive edge.
- Market Entry by Emerging Firms: Insights into how emerging firms and startups challenge established players, with their innovative approaches and agile operations.
- Collaborative Ventures: The emergence of strategic partnerships and collaborations as a means for outsourcing companies to pool resources and expand their capabilities.
Technological Advancements: Revolutionizing Outsourcing
In today’s digital age, technology is at the forefront of the outsourcing revolution. This part of the section investigates the pivotal role of technological advancements in transforming outsourcing processes. The examination covers:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): How AI is used to automate routine tasks, enhance data analysis, and drive intelligent decision-making in outsourcing operations.
- Blockchain Technology: The integration of blockchain for secure, transparent, and efficient transactions and data management in outsourcing contracts.
- Cloud Computing: The role of cloud technology in providing scalable, cost-effective infrastructure and fostering remote collaboration.
- IoT and Edge Computing: The impact of the Internet of Things (IoT) and edge computing in optimizing supply chain management and real-time data processing.
The Role of Culture in Outsourcing
Cultural Alignment: The Cornerstone of Success
Cultural alignment is a pivotal factor that influences the success of outsourcing relationships. This section explores the profound impact of cultural factors on an outsourcing company’ success. It includes:
- Cultural Compatibility: An in-depth exploration of the concept of cultural alignment and its role in creating a harmonious working environment.
- Cross-Cultural Collaboration: Insights into how organizations effectively navigate the nuances of collaborating across diverse cultural backgrounds.
- Cultural Integration Strategies: Strategies and best practices for fostering cultural alignment, including cultural sensitivity training and cross-cultural team-building activities.
Language and Communication: Bridging the Divide
The influence of language understand cultural differences on communication within global outsourcing teams is profound. This part delves into:
- Communication Challenges: An analysis of language barriers and their impact on effective verbal communication.
- Multilingual Workforce Management: Strategies for managing multilingual teams and fostering effective communication and breaking cultural barriers.
- Localization and Translation: The role of localization and translation services in overcoming language barriers and ensuring clarity in communication.
Work Ethics and Styles: Balancing Diverse Approaches
Different cultures often exhibit varying work ethics and styles that can affect project delivery and team dynamics. This section explores:
- Cultural Work Ethic Analysis: An examination of how work ethics differ across cultural barriers, cultural norms and their impact on productivity and project timelines.
- Adaptive Strategies: How businesses adapt to diverse work styles to maximize collaboration and efficiency.
- Harmonizing Work Styles: Strategies for harmonizing work styles within multinational teams, ensuring a cohesive and productive work environment.
Local Business Practices: Navigating the Cultural Business Landscape
Understanding and adapting to local business practices can be a game-changer in outsourcing partnerships. This part provides:
- Local Business Insights: An analysis of cultural nuances in business practices, including negotiation styles, decision-making processes, and business etiquette.
- Business Process Alignment: Strategies for aligning outsourcing practices with local customs, ensuring smoother collaboration and project execution.
- Legal and Regulatory Compliance: The importance of adhering to local laws and regulations to maintain a successful and legally sound outsourcing partnership.
Mitigating Cultural Challenges: Strategies for Success
Cultural challenges are an inherent part of global outsourcing. This section offers practical strategies for mitigating cultural barriers and fostering a harmonious and productive outsourcing environment. Key components include:
- Cultural Sensitivity Training: The role of training programs in building cultural awareness and sensitivity among outsourcing teams.
- Cross-Cultural Team Building: Strategies for creating a unified, culturally diverse team that leverages individual strengths.
- Conflict Resolution: Effective approaches to resolving conflicts that arise due to cultural disparities, promoting understanding and collaboration.
Understanding Cultural Competence
Cultural competence is an essential aspect of successful outsourcing. This section provides a comprehensive understanding of cultural competence, its significance in outsourcing, and the impact of cultural differences on outsourcing success.
Definition of Cultural Competence
Cultural competence refers to the ability of individuals and organizations to effectively interact and collaborate with people from different cultural backgrounds. It involves not only recognizing and respecting cultural differences but also adapting one’s behavior, communication, and practices to foster effective relationships and work harmoniously across diverse cultures. Key components of this definition include:
- Cultural Awareness: Recognizing and acknowledging the existence of various cultures, their values, customs, and belief systems.
- Cultural Sensitivity: Developing a heightened sensitivity to the needs and perspectives of individuals from different cultural backgrounds.
- Cultural Adaptability: The capacity to adjust one’s behavior, communication style, and practices to accommodate cultural differences and enhance collaboration.
Why Cultural Competence Matters in Outsourcing
The significance of cultural competence in the outsourcing realm cannot be overstated. This part of the section highlights the compelling reasons why cultural competence is crucial in outsourcing partnerships, including:
- Effective Communication: The foundation of any successful outsourcing partnership, where understanding cultural nuances is pivotal for clear and efficient communication.
- Building Trust and Rapport: How cultural competence fosters trust and rapport, which are essential for establishing strong and long-lasting outsourcing relationships.
- Conflict Resolution: The role of cultural competence in resolving conflicts that may arise from misunderstandings or differences in cultural practices.
- Maximizing Productivity: How a culturally competent workforce is more likely to work cohesively, maximizing efficiency and productivity.
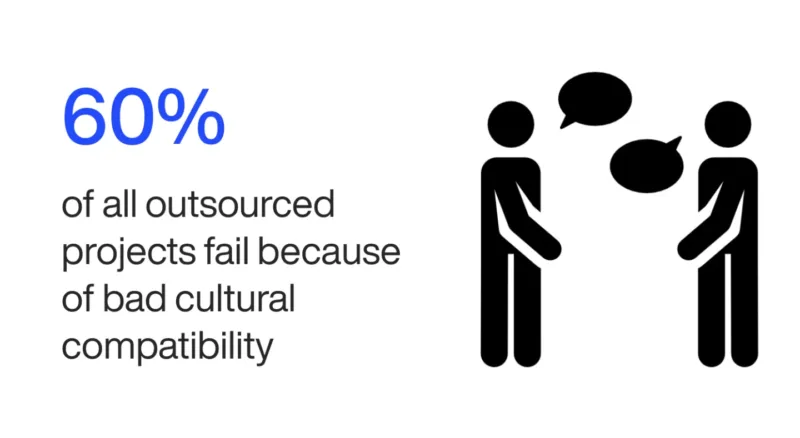
C. The Impact of Cultural Differences on Outsourcing Success
Cultural differences can significantly influence the outcome of an outsourcing project. In this segment, we delve into the various ways in which cultural disparities impact the success of outsourcing initiatives. Key aspects to be covered include:
- Communication Challenges: How language barriers and differing communication styles can impede information flow and project coordination.
- Work Ethic and Productivity: An analysis of how varying work ethics and productivity norms across cultures can affect project timelines and results.
- Project Delivery: The impact of cultural differences on project delivery, including potential delays and quality issues.
- Team Dynamics: How cultural disparities can affect team dynamics, including collaboration, motivation, and morale.
- Operational Efficiency: How cultural differences can influence the overall efficiency of outsourcing operations, potentially leading to inefficiencies and increased costs.
The Challenges of Cultural Differences
The interplay of cultural differences in the outsourcing landscape introduces a spectrum of challenges that can exert a profound impact on the success of business endeavors. In this section, we will undertake a comprehensive exploration of the prevalent cultural challenges encountered in the realm of outsourcing. Furthermore, we will draw insights from real-world case studies that provide a tangible understanding of the consequences of cultural misalignment. Finally, we will delve into the financial and operational implications of these clashes.
A. Common Cultural Challenges in Outsourcing
The arena of global outsourcing is replete with a diverse and multifaceted set of cultural challenges. These challenges arise from disparities in language, work styles, values, and communication norms among individuals and teams hailing from distinct cultural backgrounds. This section seeks to illuminate the following common cultural challenges:
1. Language Barriers: Language disparities often form an insurmountable barrier to effective communication, giving rise to misunderstandings and complications that can hinder the collaborative spirit fundamental to outsourcing.
2. Differing Work Ethic: Varying work ethics, a management style, distinct productivity expectations, and divergent approaches to time management can significantly impact the timely delivery of projects and the dynamics within teams.
3. Communication Styles: Cultural nuances extend to communication styles, impacting the ways in which individuals from diverse backgrounds interact and potentially leading to misinterpretations or miscommunications.
4. Cultural Sensitivity: Navigating cultural sensitivities and taboos presents a unique challenge, as what is considered acceptable or offensive can differ markedly across regions and cultures.
5. Conflict Resolution: Differing approaches to conflict resolution implicit communication can escalate misunderstandings and disputes, posing a significant challenge in managing and resolving conflicts in culturally diverse teams.
B. Case Studies Highlighting the Consequences of Cultural Misalignment
The lessons learned from real-world experiences are invaluable in shedding light on the tangible consequences of cultural misalignment in outsourcing partnerships. This section will draw from illustrative case studies, revealing the challenges faced, the issues encountered, and the valuable insights derived from these situations:
1. Communication Breakdowns: Case studies will underscore how cultural miscommunication can give rise to project delays, misunderstandings, and hinder efficient information exchange.
2. Conflict Escalation: Instances will be presented where cultural misunderstandings escalated into significant conflicts, casting a shadow on the outsourcing relationship and complicating matters further.
3. Loss of Productivity: These examples will illuminate how cultural clashes within teams can lead to decreased productivity, negatively impacting project outcomes.
4. Project Failures: Case studies will exemplify how cultural misalignment contributed to project failures or suboptimal results, highlighting the importance of cultural fit and competence in project management.
C. The Financial and Operational Implications of Cultural Clashes
In the complex landscape of outsourcing, it is vital to comprehend the financial and operational implications that stem from cultural clashes. This section will address the concrete and intangible costs associated with cultural misalignment, for example, including:
1. Cost Overruns: The ramifications of cultural clashes, such as project delays, inefficiencies, and rework, can result in increased project costs and budget overruns.
2. Resource Drain: Conflicts, misunderstandings, and inefficient collaboration, driven by cultural misalignment, can deplete organizational resources and divert focus from core activities.
3. Reputation Damage: Cultural misalignment can tarnish an organization’s reputation, potentially jeopardizing future outsourcing opportunities and damaging the brand image.
4. Employee Retention: Disengagement among team members grappling with cultural challenges can impact morale and retention rates, necessitating additional resources for recruitment and training.
5. Client Satisfaction: Cultural misalignment can adversely affect client satisfaction, potentially leading to contract terminations and revenue loss, underscoring the far-reaching consequences of cultural clashes in outsourcing.
Strategies for Enhancing Cultural Competence
In order to effectively tackle the complexities arising from cultural differences in the realm of outsourcing, it is crucial to craft and execute strategies that bolster cultural competence. This section will thoroughly explore these strategies, encompassing the provision of training and education for outsourcing teams, the construction of diverse and inclusive teams, and the cultivation of cultural sensitivity and awareness among remote workers.
Training and Education for Outsourcing Teams
Training and education play a central role in elevating cultural competence within outsourcing teams. This subsection underscores the significance of training and educational initiatives and their contribution to cultural competence. It encompasses:
1. Cultural Awareness Training: This facet entails enlightening team members about the diverse cultural nuances that exist and instilling an appreciation for these distinctions. By doing so, it fosters mutual understanding and empathy among team members, laying a strong foundation for harmonious collaboration.
2. Cross-Cultural Communication Training: The development of effective communication skills across an array of cultures is pivotal. By enhancing the capability of team members to bridge the language barrier and communication gaps, this training promotes clearer communication and minimizes misunderstandings.
3. Conflict Resolution Training: Cultural misunderstandings or differences in conflict resolution styles can lead to disputes. Training in conflict resolution strategies equips team members to manage and resolve these conflicts effectively, promoting smoother working relationships.
4. Cultural Competence Workshops: Workshops that are specifically designed to nurture cultural competence offer interactive activities and real-world case studies. These activities expose team members to practical scenarios, enriching their ability to adapt to cultural diversity and address challenges proactively.
Building Diverse and Inclusive Outsourcing Teams
The establishment of diverse and inclusive outsourcing teams in house team forms the bedrock for enhancing cultural competence. This section highlights the significance of diversity and inclusion and elucidates the methods by which organizations can enact these principles:
1. Recruitment and Hiring Practices: Organizations must reevaluate their recruitment and hiring practices, with the aim of attracting talent from diverse cultural backgrounds. By actively seeking diversity, they can enrich their talent pool and cultivate a culturally rich workforce.
2. Cultural Diversity Metrics: The adoption of metrics for tracking and measuring cultural diversity is a pivotal step towards ensuring organizations are making progress in their pursuit of inclusive teams. Metrics offer a quantifiable means of assessing and enhancing cultural diversity.
3. Inclusive Leadership: Leadership that champions inclusivity is of paramount importance. Inclusive leaders ensure that every team member, irrespective of their cultural background, feels valued and respected. They set the tone for fostering an environment of acceptance and cooperation.
4. Cross-Cultural Collaboration: Strategies aimed at encouraging cross-cultural collaboration are indispensable. Such strategies facilitate the exchange of knowledge and insights among team members, promoting the communication schedule the celebration of unique cultural perspectives and the generation of innovative solutions.
Developing Cultural Sensitivity and Awareness
Cultural sensitivity and awareness are fundamental elements of cultural competence. This subsection delves into the cultivation of these attributes, emphasizing their importance and providing strategies for their development:
1. Cultural Sensitivity Training: Training programs dedicated to enhancing team members’ sensitivity to cultural nuances and the needs of their colleagues are essential. These programs instill an acute awareness of cultural subtleties and help team members navigate the complexities of cultural diversity.
2. Cross-Cultural Experiences: The value of promoting cross-cultural experiences, such as international assignments, cannot be overstated. These experiences expose team members to different cultures and foster cultural awareness. They provide firsthand insights into the diversity of global perspectives.
3. Cultural Intelligence: The concept of cultural intelligence (CQ) encapsulates the ability to work effectively in diverse cultural contexts. Organizations can assess and cultivate this intelligence among their team members, thereby enhancing their capacity to navigate cross-cultural and social interactions well.
4. Cultural Competence Assessment: The role of cultural competence assessments is indispensable in the journey towards developing and strengthening awareness and sensitivity. Such assessments provide a means of evaluating and improving team members’ cultural competence.
Bridging the cultural gap in outsourcing is a multifaceted endeavor that necessitates the adoption of best practices and strategies. In this comprehensive section, we explored the essence of cultural competence, the importance of understanding cultural differences, and the impact of cultural disparities on outsourcing success. We delved into common cultural challenges faced in the outsourcing landscape, highlighted real-world case studies to underscore the consequences of cultural misalignment, and scrutinized the financial and operational implications of these clashes.
To mitigate these challenges, we presented strategies for enhancing cultural competence. These strategies encompassed training and education for outsourcing teams, building diverse and inclusive teams, and developing cultural sensitivity and awareness. By imparting cultural awareness, cross-cultural communication skills, and conflict resolution training, organizations can foster more effective and harmonious relationships in the global outsourcing arena. Embracing diversity in team composition, nurturing trust and respect, and harmonizing conflict resolution processes were identified as essential components of this journey.
Finally, we explored the best practices for bridging the cultural gap, highlighting effective communication techniques, building strong working relationships with offshore partners, and leveraging technology and tools to enhance cultural competence. These practices promote clear and efficient communication, foster strong collaborations, and utilize technology to facilitate cultural understanding, ensuring that cultural competence is a driving force in the success of outsourcing initiatives. Cultivating cultural competence is not just a strategy; it is a cornerstone of success in today’s globalized business environment, where diversity and understanding are key to achieving business goals and expanding horizons.



Leave A Comment
You must be logged in to post a comment.