Organizations often have to make important decisions that significantly impact their operations, efficiency, and bottom line. Among these decisions, one stands out as constant: whether to outsource or manage specific functions in-house. From cost and expertise to control, scalability, and customer impact, the decision between outsourcing and in-house operations is far from simple.
In his comparative analysis, we delve into the complexities of outsourcing versus in-house, evaluating the benefits and drawbacks of each option and providing insights to help businesses make better decisions aligned with their resources and goals.
Some Notable Stats:
- 50% of surveyed executives identify talent acquisition as the top internal challenge in meeting their organization’s strategic priorities.
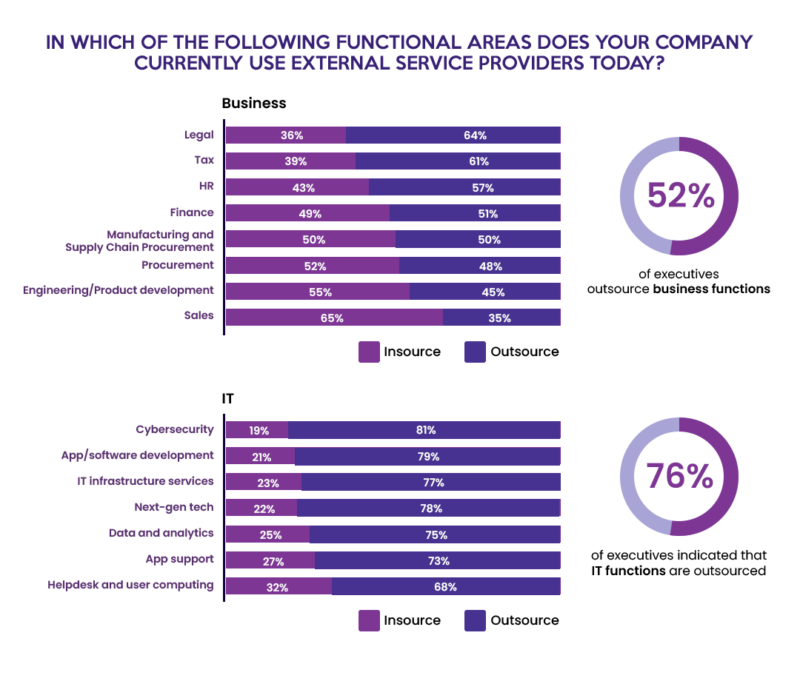
- 52% of executives outsource business functions like Legal, Tax, and HR.
- 76% of surveyed executives say their company uses external service providers for IT functions such as Cybersecurity, App/software development, and IT Infrastructure services.
- 57% indicate the primary driver of Traditional Outsourcing is cost reduction, typically via staff augmentation for transactional business and IT activities.
- 75% of companies leverage data and analytics via external providers.
Outsourcing: Pros and Cons
Advantages of Outsourcing
Cost savings
Outsourcing to locations with cheaper labor costs, such as Asia or Eastern Europe, can significantly reduce employee-related expenses, such as salaries, benefits, and insurance. It also eliminates the need to invest in office space, equipment, and infrastructure, resulting in lower overhead costs.
Access to specialized expertise
Outsourcing providers are often experts in their fields, providing access to expertise that may not be available in-house. These outside experts bring a wealth of knowledge and experience, often excelling in their particular industries. By leveraging the expertise of an outsourced team, businesses can easily complete complex tasks and projects without having to spend on extensive training or hiring additional in-house personnel.
Focus on Core Competencies
Businesses can focus their resources on core business functions and strategic initiatives by outsourcing non-core tasks. This enhanced focus allows businesses to nurture their capabilities and drive innovation while the outsourcing team handles specialized tasks efficiently and effectively.
Scalability and flexibility
Outsourcing enables companies to scale up or down in response to changing demand. They can easily add or reduce resources and services depending on the demands. During peak seasons, a company can quickly increase its customer support staff and then scale it back after the demand has subsided.
Disadvantages of Outsourcing
Loss of control
A company gives up some control and decision-making power when it outsources certain tasks or processes to external service providers. This can make it challenging for them to ensure that the outsourced work aligns with the organization’s standards, strategic goals, and operational preferences.
Communication challenges
When a company works with third-party service providers in different countries, language barriers, cultural differences, and time zone differences are often experienced. These issues can hinder effective communication and collaboration. Miscommunications, delays in response times, and difficulties in communicating complex information can all happen, potentially leading to misaligned expectations and project setbacks.
Quality control issues
Entrusting tasks to an outsourcing company can result in limited visibility and control over the quality of work delivered. The outsourcing partner may have different standards or processes, which can result in variations in quality that are not aligned with the company’s expectations. Maintaining consistent quality across outsourced functions can be difficult, especially when the organization relies on the service provider’s internal quality control systems.
Dependency on external partners
Relying too heavily on outsourced partners can create vulnerabilities. The outsourcing company’s operations may be disrupted if the external partner faces instability, management changes, or other challenges. This reliance can hinder a company’s ability to adapt to shifting market conditions.
In-house Operations: Pros and Cons
Advantages of In-house Operations
Control and oversight
Companies with in-house operations have greater control and oversight over their processes and activities. When an internal team manages critical functions, decision-makers have direct control over every aspect of these activities, from hiring and training people to establishing and enforcing quality standards. This level of control enables quick modifications, immediate responses to changing conditions, and the capacity to align operations with the company’s strategic goals closely.
Alignment with company culture and values
It is easier to foster a consistent corporate culture that reflects the company’s mission, vision, and values when processes and functions are kept within the organization. In-house teams tend to have a better understanding of the company’s goals and principles, which fosters a sense of loyalty and commitment. This can result in increased employee morale, better teamwork, and a stronger sense of purpose, eventually contributing to a more cohesive and motivated workforce.
Enhanced security and control
Security and confidentiality are improved when data and critical functions are managed internally. The company has direct control of its IT infrastructure, data storage, and cybersecurity measures, allowing it to enforce effective security standards suited to its specific needs. This reduces the chances of data breaches, intellectual property theft, and unauthorized access.
Disadvantages of In-house Operations
Higher upfront costs
One notable disadvantage of in-house operations is the higher upfront costs of building and maintaining internal processes and infrastructure. Companies must invest in facilities, equipment, technology, and personnel, incurring substantial initial expenses. These can strain financial resources, especially for startups and small businesses. However, while the initial expenditure is significant, in-house operations may give cost advantages over time if the company can achieve economies of scale, enhance efficiency, and maintain control over costs in the long term.
Limited scalability
In-house teams and departments often have limited resources, such as office space, equipment, and staff, making it difficult to respond quickly to changing business conditions. When a company experiences rapid growth, seasonal fluctuations, or the need for additional expertise, it may find it challenging to scale its in-house operations efficiently. This constraint can lead to higher expenses, delayed project delivery, and missed expansion opportunities.
Recruitment and training challenges

Finding qualified applicants, holding interviews, and onboarding new employees all need time and effort to create and sustain an efficient in-house team. This can be time-consuming and costly, delaying filling critical positions, particularly those needing specific skills or knowledge. Furthermore, continuous training is necessary to keep the team updated with industry trends and evolving technologies after hiring employees. Not addressing these challenges can lead to high turnover rates, skill gaps, and increased labor costs.
Factors Influencing the Decision
Nature of the task or project
Complex and specialized jobs that require a high level of expertise and resources are often suited for outsourcing to service providers that can deliver superior results. On the other hand, tasks related to the organization’s core competencies may be more suited for in-house management because they directly contribute to the company’s competitive advantage. Short-term or one-time initiatives may be outsourced for efficiency; long-term, strategic functions may be kept internally to maintain control and align with the company’s more extensive goals. Finally, whether outsourcing or in-house development is the most effective way to achieve desired results depends on the nature of the work or project.
Cost considerations
Cost considerations are important in deciding whether to outsource or keep operations in-house. Companies must carefully consider the financial implications of each option, including labor costs, infrastructure expenses, equipment, and continuous operational costs. Outsourcing can help save costs, especially when labor is cheaper in other regions, and it reduces the need for large upfront investments in infrastructure. On the other hand, in-house operations may provide better cost control over time, particularly for tasks critical to the company’s core operations. Whether to outsource or keep it in-house hinges on the balance of initial investment, ongoing operational costs, and the possible long-term benefits of each option, with cost considerations playing a critical role in the evaluation.
Risk Assessment
Companies must assess the risks associated with outsourcing and keeping the operations in-house. For instance, outsourcing can introduce risks such as data breaches, loss of control over processes, or dependencies on external service providers. In contrast, in-house operations may carry risks related to employee management or regulatory compliance. The decision depends on the company’s risk tolerance and ability to manage and mitigate risks.
Strategic goals
The organization’s strategic goals are critical in assessing whether it should outsource or keep a specific function or process in-house. The task’s alignment with the organization’s broader strategic objectives is essential. Functions critical to the company’s core competencies and directly contribute to its competitive advantage are frequently kept in-house to preserve control and ensure close alignment with strategic goals. Non-core functions may be good candidates for outsourcing, allowing the company to focus its internal resources and attention on strategic initiatives that drive business growth and market competitiveness.
Technology and Innovation
Outsourcing often provides access to innovative technologies and specialized skills that organizations may not have in-house. Outsourcing companies are usually at the forefront of technical breakthroughs, delivering cutting-edge tools and processes. This can be especially useful for jobs that require expertise or the latest technology, such as IT support or software development projects. In contrast, in-house operations may require significant technological investments and continuous efforts to stay updated with the latest developments.
Employee Impact
Outsourcing can directly impact the existing workforce, potentially resulting in job redundancy or changes in job roles. These decisions can affect employee morale and job security. On the contrary, in-house operations may provide more job stability and opportunities for professional development within the organization. When deciding between in-house vs. outsourcing, it is often necessary to consider the impact on employees, which may include retraining, reassignment, or open communication about the reasons behind the decision. In making the decision, it is critical to balance the organization’s strategic goals with the well-being of the employees.
Making the Decision
Conducting a thorough cost-benefit analysis
A comprehensive cost-benefit analysis is often necessary when deciding whether to outsource or keep the tasks or development process in-house. This step requires thoroughly evaluating each option’s costs and potential advantages.
On the cost side, companies should examine costs like labor, infrastructure, equipment, training, and ongoing operational costs for in-house operations. When considering outsourcing, they should evaluate the rates offered by service providers, including any hidden or unforeseen costs.
On the benefits side, the potential advantages of outsourcing, such as cost savings, access to specialized expertise, scalability, and reduced administrative responsibilities, must be weighed. On the other hand, in-house operations provide control, alignment with key strengths, and stronger integration with the company’s culture and values.
Comparing these costs and benefits will help businesses make informed decisions that align with their financial and strategic goals. This will serve as a guide toward the most economically sound and strategically advantageous choice.
Considering the impact on company culture and values
In-house operations often promote a company culture strongly aligned with the organization’s values, mission, and identity. Employees have the same sense of purpose and commitment to the organization’s goals. On the contrary, outsourcing might create cultural gaps when working with external service providers, compromising organizational cohesion and values alignment.
Companies must balance the importance of their current culture with the potential benefits of outsourcing. While outsourcing can help save costs, it could threaten cultural harmony. Some companies choose to retain critical functions to maintain a strong in-house culture.
Choosing between outsourcing and in-house operations is a complex decision that is impacted by a wide range of factors. This comparative analysis has shed light on the advantages and drawbacks of each strategy, providing helpful information to navigate this critical decision-making process. The factors at play, ranging from the nature of the task, cost considerations, technology, and employee impact, highlight the importance of a well-informed choice that supports the organization’s strategic goals and operational requirements. Whether outsourcing software development or customer support, partnering with an external service provider assists companies in navigating the complexities of these functions efficiently. There is no one-size-fits-all solution; each decision should be tailored to each function or process’s specific circumstances and needs.



Leave A Comment
You must be logged in to post a comment.